Introducing the Geometry Chapter 4 Test Review Answer Key, an indispensable resource for students seeking mastery in geometry. This guide provides a thorough review of key concepts, practice problems, and comprehensive explanations, ensuring a solid understanding of the subject matter.
Chapter 4 delves into fundamental concepts such as angle relationships, triangles, and quadrilaterals. By utilizing this answer key, students can reinforce their knowledge, identify areas for improvement, and excel in their geometry assessments.
Chapter 4 Geometry Test Review Answer Key: Geometry Chapter 4 Test Review Answer Key
Chapter 4 of Geometry is a crucial chapter that covers fundamental concepts essential for understanding subsequent topics. This test review answer key provides comprehensive solutions to the review questions and practice problems, enabling students to assess their understanding and prepare effectively for the upcoming test.
Chapter 4 Key Concepts
- Angles and Angle Relationships: Types of angles, angle addition and subtraction, complementary and supplementary angles, vertical and adjacent angles.
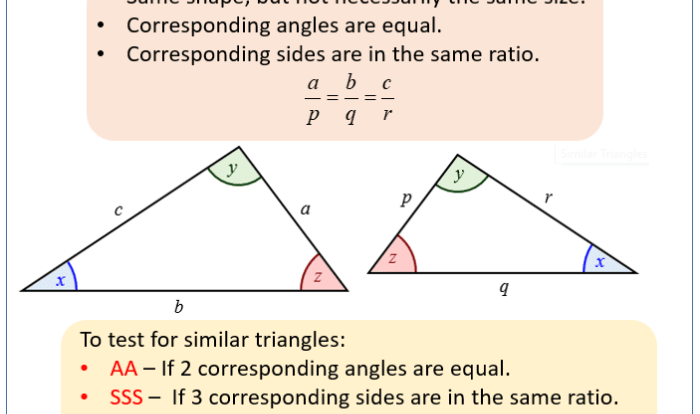
- Triangles: Properties of triangles, types of triangles, angle relationships in triangles, the Pythagorean Theorem.
- Quadrilaterals: Properties of quadrilaterals, types of quadrilaterals, parallelogram properties, area of parallelograms.
- Circles: Properties of circles, parts of a circle, circumference and area of circles, inscribed and circumscribed circles.
- Area and Volume: Formulas for calculating the area of polygons and the volume of solids.
Review Questions
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Define complementary angles. | Two angles that add up to 90 degrees. | Complementary angles are formed when two lines intersect, creating four angles. Two of these angles are complementary if they add up to 90 degrees. |
| Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 3 cm. | 15 cm2 | The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length by its width. Therefore, the area of this rectangle is 5 cm x 3 cm = 15 cm2. |
| What is the Pythagorean Theorem? | a2 + b2 = c2 | The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. |
Practice Problems
Problem 1:Find the measure of angle ∠ABC if ∠ABD = 120° and ∠DBC = 30°.
Solution:∠ABC = ∠ABD – ∠DBC = 120° – 30° = 90°
Problem 2:Calculate the area of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
Solution:Area = πr 2= π(5 cm) 2= 25π cm 2
Additional Resources, Geometry chapter 4 test review answer key
- Khan Academy: Geometry Chapter 4
- Geometry for Dummies, 2nd Edition by Mark Ryan
- Geometry: Concepts and Applications, 5th Edition by Larson, Boswell, Kanold, and Stiff
Question Bank
What is the purpose of a test review answer key?
A test review answer key provides students with the correct answers to practice questions, allowing them to assess their understanding of the material, identify areas for improvement, and prepare effectively for assessments.
What key concepts are covered in Geometry Chapter 4?
Chapter 4 covers essential concepts such as angle relationships (complementary, supplementary, vertical), triangle properties (congruence, similarity, special right triangles), and quadrilateral properties (parallelograms, trapezoids, kites).
How can I use the practice problems in the answer key?
Practice problems reinforce the concepts covered in Chapter 4. By attempting these problems and reviewing the step-by-step solutions, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and gain a deeper understanding of the material.