Lesson 2 find the area of triangles and other polygons – Embark on an enlightening journey through lesson 2: finding the area of triangles and other polygons. This chapter delves into the fascinating world of geometry, equipping you with essential formulas and techniques to determine the surface area of these fundamental shapes.
Whether you’re an aspiring architect, an inquisitive engineer, or simply seeking to expand your mathematical knowledge, this lesson promises an enriching and practical experience.
From understanding the intricacies of triangles to exploring the diverse properties of polygons, this comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation in geometric measurement. Prepare to unravel the secrets of these geometric wonders and unlock their countless applications in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Triangles
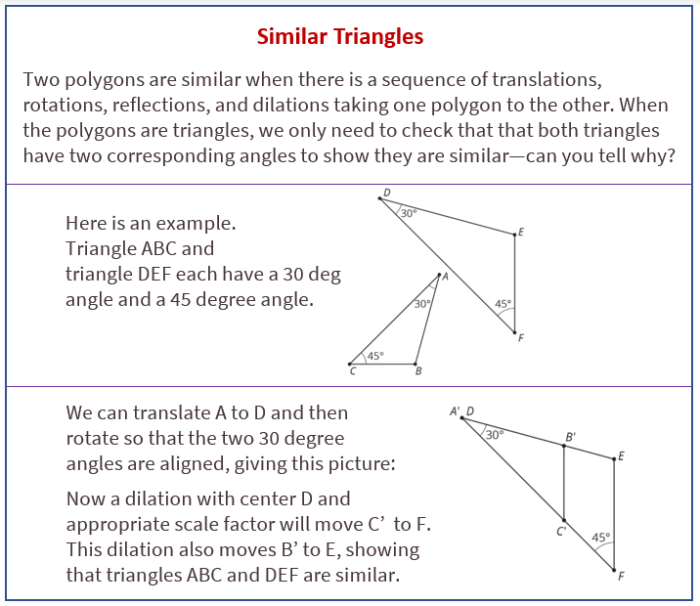
Triangles are three-sided polygons with three interior angles that add up to 180 degrees. They are classified based on the lengths of their sides and the measures of their angles.
Types of Triangles:
- Equilateral Triangle:All three sides are equal in length, and all three angles measure 60 degrees.
- Isosceles Triangle:Two sides are equal in length, and the angles opposite those sides are equal.
- Scalene Triangle:All three sides are different lengths, and all three angles are different measures.
Examples of Triangles in Real-World Objects:
- Rooftops
- Road signs
- Pizza slices
Finding the Area of Triangles
The area of a triangle is given by the formula: Area = 1/2 – base – height.
Steps to Find the Area of a Triangle:
- Identify the base and height of the triangle.
- Substitute the values of the base and height into the formula.
- Calculate the area using the formula.
Polygons and Their Properties
Polygons are closed, two-dimensional figures with straight sides. They are classified based on the number of sides they have.
Types of Polygons:
- Quadrilateral:Four sides
- Pentagon:Five sides
- Hexagon:Six sides
- Heptagon:Seven sides
- Octagon:Eight sides
Examples of Polygons in Real-World Objects:
- Soccer balls (hexagons and pentagons)
- Dice (hexagons)
- Stop signs (octagons)
Finding the Area of Other Polygons: Lesson 2 Find The Area Of Triangles And Other Polygons
The area of a polygon can be found by dividing it into triangles and finding the sum of the areas of those triangles.
Steps to Find the Area of a Polygon:
- Divide the polygon into triangles.
- Find the area of each triangle using the formula: Area = 1/2
- base
- height.
- Sum the areas of all the triangles to find the total area of the polygon.
Applications in Real-Life Scenarios
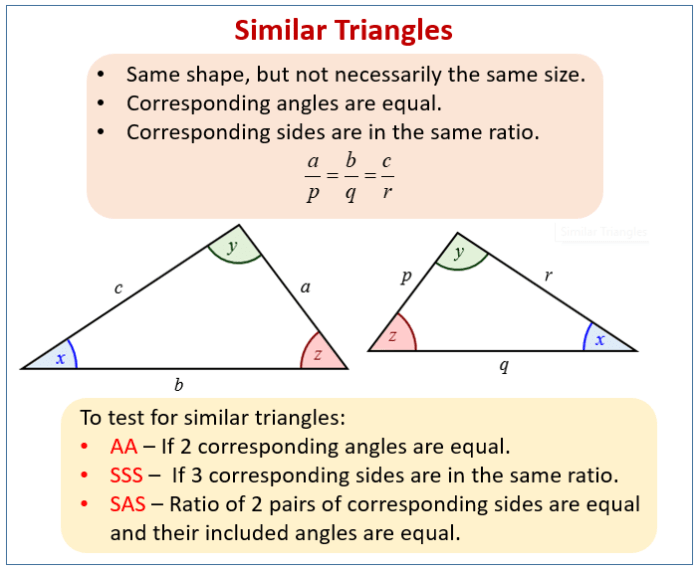
Finding the area of triangles and polygons is used in various fields, including:
- Architecture:Calculating the area of rooms, buildings, and other structures.
- Engineering:Determining the area of bridges, dams, and other structures.
- Design:Creating patterns, logos, and other graphic designs.
Questions Often Asked
What is the formula for finding the area of a triangle?
The formula for finding the area of a triangle is A = 1/2 – base – height, where ‘base’ represents the length of the triangle’s base and ‘height’ represents the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
How do I find the area of a polygon with an irregular shape?
To find the area of a polygon with an irregular shape, divide the polygon into triangles and calculate the area of each triangle. Then, add the areas of all the triangles to find the total area of the polygon.
What are the different types of polygons?
There are many different types of polygons, including quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), and so on. Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides, the length of their sides, and the angles between their sides.